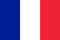
What causes warts
- When using other people’s personal hygiene products and commonly used items;
- In public places (swimming pools, bathhouses, etc. ), especially when walking barefoot;
- If the skin is injured;
- Increased sweating of hands and feet;
- Contact with an infected person (handshake, sexual contact, etc. );
- Walking in tight, uncomfortable shoes can cause the skin on your feet to rub;
- When using non-sterile instruments (in beauty salons, etc. ).
Are warts always dangerous?
How to Identify Warts: Signs and Symptoms
- Moles are dark or black, while warts are light-colored;
- Warts grow closely together with the skin, moles are separate structures, as if glued to the body;
- Moles feel soft and smooth, while warts feel hard, hard and rough.
What is the structure of benign tumors?
Common (simple, vulgar) warts
Why do benign structures appear on the skin?
- Injuried;
- Virus;
- Systemic diseases of the body, such as xanthomas, occur due to excess fat in the blood;
- long-term skin disease;
- exposure to corrosive substances;
- overexposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- X-ray;
- Genetic (e. g. seborrheic dermatoses).
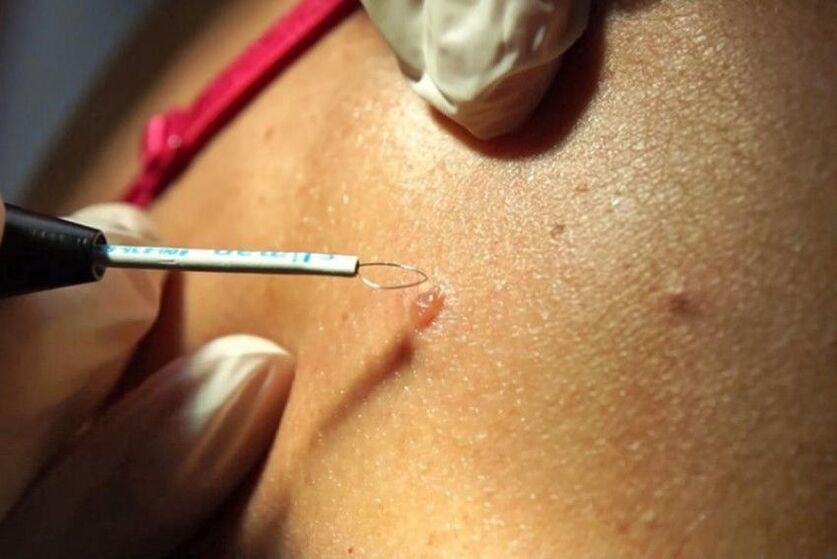
Plantar (apical) warts
- simple;
- A week;
- mosaic.
Are benign forms hiding dangers?
periungual plantar warts
Where do warts come from – they are contagious!
Mosaic plantar warts
Benign and Malignant Tumors of the Skin: What’s the Difference?
Flat (juvenile) warts
- Mild – one or a few painless warts;
- Medium – 10 to 100 painless growths;
- Severe - more than 100 tumors.
Laser wart removal
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) laser. Surgery with this laser is more painful. While the carbon dioxide laser seals blood vessels, it also kills wart tissue. In the process, it is possible to damage healthy tissue. Wounds usually take longer to heal and scarring may form. The efficiency is about 70%.
- Erbium laser. It is characterized by shorter wavelength. The likelihood of scarring after healing is significantly reduced.
- Pulsed dye laser. This laser can more effectively seal the blood vessels that feed the wart. It doesn’t damage as much healthy tissue as CO2 laser does. It is also the only type of laser approved for use in children. This treatment is approximately 95% effective.
| advantage | defect |
| Scarring is extremely unlikely (depending on how neglected the pathology is) | high price |
| Rapid tissue healing | |
| This method is highly efficient | |
| Minimal damage to healthy tissue | |
| Program speed |
Treatment of filiform papilloma
Official methods and treatments
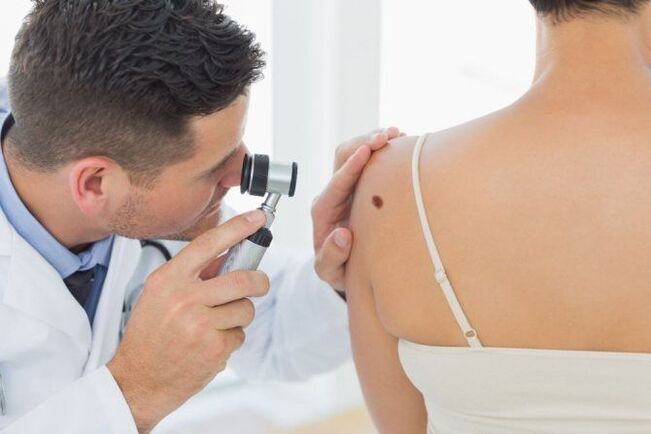
Remove with radio knife
- Completely painless;
- the speed of the program;
- Rule out edema and infiltration;
- No postoperative complications;
- There will be no scarring at the site where the wart was removed;
- Rapid recovery period.
Prevent skin tumors
- If a tumor appears on your skin, contact your doctor immediately;
- It should be removed only after expert and diagnostic confirmation that it is benign;
- Avoid overexposure to sunlight;
- Use sunscreen, especially if you are prone to moles and hyperpigmentation;
- No exposure to chemically active substances and carcinogens;
- Avoid foods that may cause cancer (bacon, sausages, animal fats, meat products containing food stabilizers).